A High-Level Overview of a Television Campus with ST 2110 Summary Campus architecture: Single-fabric design with PTP, media, and control planes Sources & destinations: Cameras, encoders, playout as sources; monitors, decoders, recorders as destinations Media flows: ST 2110-20 (video), ST 2110-30 (audio), ST 2110-40 (ANC/data), all over RTP multicast PTP: IEEE 1588-2008 PTPv2 with grandmaster, boundary clocks, and sync to every device Switch orchestration: NMOS IS-06 / SDN for flow provisioning; IGMP, PIM, QoS on switches Switch design: VLANs, DSCP mapping, PTP-aware ports, and full configuration examples Note: This article describes a full end-to-end ST 2110 television campus: timing (PTP), sources/destinations, switch orchestration, and concrete switch structures and configurations.

Monitoring SMPTE ST 2110 Systems: A Deep Dive with Prometheus, Grafana, and Beyond Summary Why Monitor ST 2110: Real-time requirements, packet loss detection, timing accuracy, and business continuity Critical Metrics: RTP stream health, PTP synchronization, network bandwidth, buffer levels, and SMPTE 2022-7 protection switching NMOS Control Plane: Monitoring IS-04 registry, IS-05 connections, node health, and resource integrity Prometheus Architecture: Time-series database, exporters, PromQL queries, and alerting framework Custom Exporters in Go: Building ST 2110-specific exporters for RTP analysis, PTP status, and gNMI network telemetry gNMI for Modern Switches: Streaming telemetry with sub-second updates replacing legacy SNMP polling Grafana Dashboards: Real-time visualization, alert panels, and production-ready dashboard templates Scale Strategies: Federation, Thanos, cardinality management for 1000+ streams Alternative Solutions: ELK Stack, InfluxDB, Zabbix, and commercial tools (Tektronix Sentry, Grass Valley iControl) Production Best Practices: High availability, security hardening, CI/CD automation, and compliance requirements Note: This article provides production-ready monitoring strategies for both data plane (ST 2110) and control plane (NMOS) in broadcast systems.
AMWA NMOS: Building the Control Plane for SMPTE ST 2110 with Go Summary NMOS Overview: Open specifications for networked media control and management IS-04: Discovery and Registration of devices and resources IS-05: Device Connection Management for automated routing IS-06: SDN control for switches and network infrastructure IS-08: Channel Mapping for audio routing within devices IS-09: System Parameters for global network timing Go Implementation: Production-ready NMOS client and registry server Real-world Use Cases: Automated workflows, resource discovery, connection management, SDN integration Note: This article provides comprehensive coverage of AMWA NMOS specifications with practical Go implementations.
Building WebAssembly Applications with Go: A Complete Guide WebAssembly (WASM) has revolutionized web development by allowing high-performance code to run in browsers at near-native speed. Go, with its excellent tooling and straightforward syntax, is an ideal language for building WASM applications. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how to create, optimize, and deploy WebAssembly applications using Go.
TL;DR WebAssembly: Binary instruction format for browsers, enabling near-native performance Go + WASM: Compile Go code to WASM for browser execution Key Benefits: Performance, code reuse, type safety, and modern tooling Use Cases: Image processing, games, data visualization, cryptography, and more Production Ready: Complete examples with optimization techniques 1.
Building Production-Ready SRT Gateway with Go Summary SRT Protocol: UDP-based secure and reliable transport protocol for live streaming Go Implementation: High-performance SRT server with concurrent connection handling Production Ready: Authentication, encryption, statistics, and monitoring Low Latency: Sub-second latency for broadcast-quality streaming Use Cases: Live news, sports broadcasting, contribution links, remote production Note: This article provides a complete implementation guide for an SRT gateway server used in production broadcast environments. All code examples are based on real-world scenarios and have been tested in live systems.
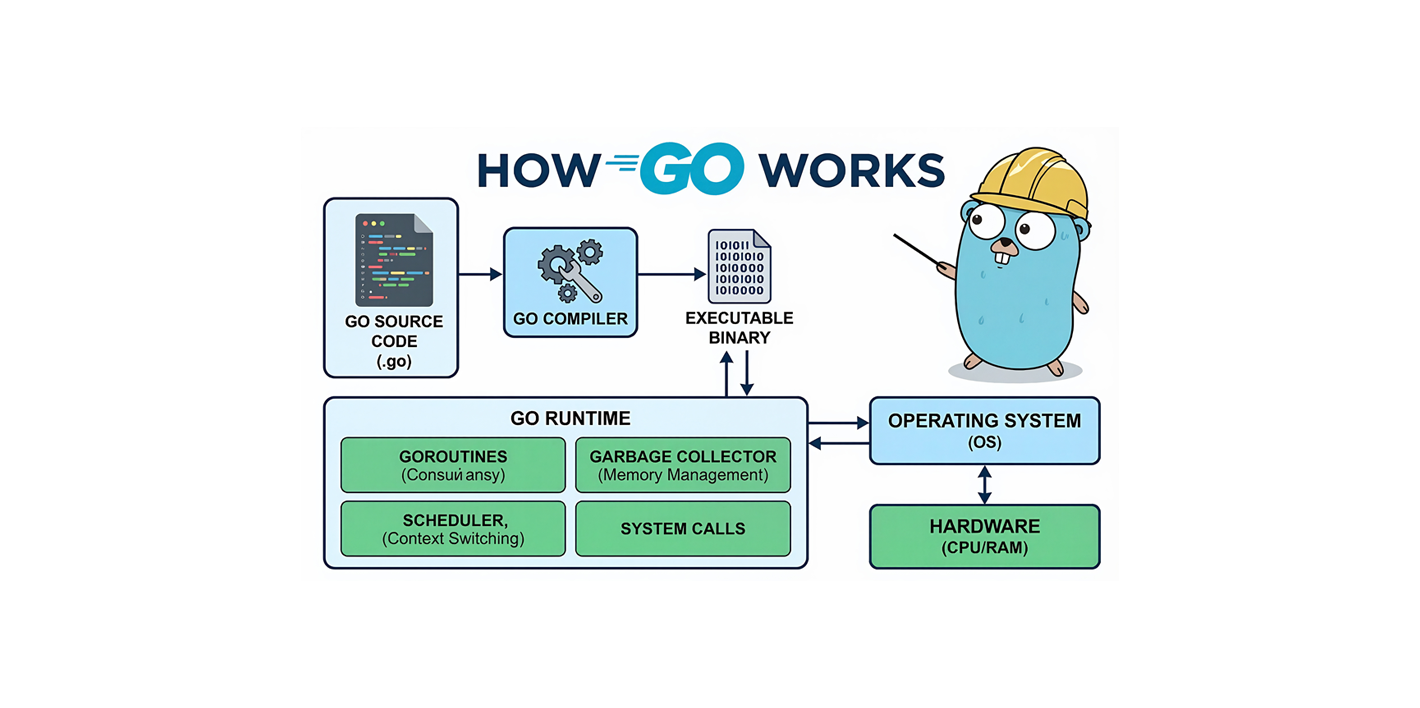
How Go (Golang) Works? Go (Golang) is a programming language developed at Google, designed to meet modern software engineering needs. In this article, we’ll examine Go’s execution model in depth—from compilation to runtime internals, from goroutines to garbage collection.
Summary Compilation pipeline: Lexer, parser, type checker, SSA, code generation Runtime internals: Scheduler (M:P:G), memory manager, garbage collector Concurrency model: Goroutines, channels, select Performance: Native binary, low latency, high throughput Production ready: Case studies, debugging scenarios, optimization techniques Note: This article is a deep dive into the Go runtime.
Real-Time Video Analysis and Edge Processing with Go Summary Edge Processing: Processing data locally without sending it to the center Go + Video Pipeline: High-performance video processing with goroutine and channel structure Production Ready: Motion detection, object detection, event publishing, monitoring Cost Savings: 95%+ savings compared to cloud processing Note: This article shares the core components of a video analysis system used in production. Code examples and architectural decisions are based on real project experiences.
The Power of Golang with gRPC: High-Performance Microservice Communication - A Modern Approach TL;DR gRPC: High-performance RPC framework developed by Google, using HTTP/2 and Protocol Buffers Go + gRPC: Ideal combination for concurrency and performance 4 Communication Models: Unary, Server Streaming, Client Streaming, Bidirectional Streaming Production Ready: Auth, Load Balancing, Health Checks, Monitoring support 1. Introduction: Modern Solution to Communication Challenges in the Microservice Era In the modern software ecosystem, microservice architectures have created a revolution to overcome the limitations of monolithic structures.
Modern API Protocols: A Comprehensive Review with Go TL;DR REST: Simple integration, broad client support; great for CRUD and public APIs. gRPC: Low latency, high throughput; best for microservice-to-microservice. GraphQL: Flexible querying and single endpoint; frontend/mobile heavy apps. WebSocket: Real-time, bidirectional; chat, trading, collaboration, games. Webhook: Event-driven integrations and automation. gRPC‑Web: Browser-friendly gRPC via gateway; type-safe and fast. tRPC: End-to-end type safety in TypeScript stacks; rapid dev. Quick Selection Guide Need real-time?
High-Performance Messaging Systems with Apache Kafka and Go: Architecture, Optimization, and Practical Solutions Apache Kafka stands as one of the most powerful and efficient distributed messaging systems in modern data architectures, offering an ideal solution for developing high-performance applications. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the technical architecture behind Kafka’s exceptional performance and demonstrate its effective implementation with Go programming language through detailed examples and real-world scenarios.
🏗 Kafka’s Performance Architecture Let’s demonstrate Kafka’s basic architecture with the following diagram: